Say Hello to Hailey Hopping Hare
I’m Hailey the Hopping Hare, I’m the skip-counting master.
This is a skill that helps to count things faster;
Learn to count up or down by a number other than one.
Quick like a bunny, you soon will be done.
Keep in mind that skip counting is repeated addition.
Moving swiftly through problems is my main mission.
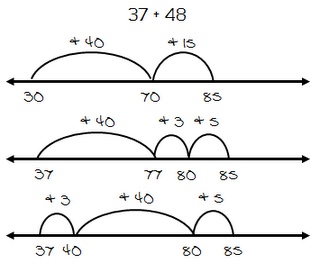
WHAT is hopping? Students use place value and number sense to add or subtract numbers. Students first start with the bigger number in the problem; this number is the starting point for hopping. Then they decompose or break apart the second number by place value (into 10’s and 1’s). Depending on the problem, students will either add or subtract, hopping first by 10’s and then by 1’s. Students label numbers above hops to help ensure solution is correct. Read more about Hailey’s strategy below or download the complete unit here.
WHY is hopping important? When students use the hopping strategy, they are essentially skip-counting by 10’s and 1’s. This helps strengthen mental computation, builds number sense and solidifies foundational place value skills. It also serves as an efficient method for students to double-check solutions. Furthermore, hopping can easily be extended to larger numbers and multi-step problems because it tracks mathematical thinking and steps taken to complete problem.
HOW do I teach hopping? Teach hopping in isolation first so that students become familiar with the process of identifying larger number and decomposing smaller number by place value. Use patterned, pre-labeled or open number lines until students can proficiently count and track hops (see examples). After proficiency is demonstrated, introduce an open number line where students determine the starting point then draw and label hops without support.
WHEN should I use hopping? This is an ideal strategy for developing mathematicians who have a solid place value and number sense foundation. It is most effective to introduce the hopping strategy after students become proficient with the counting strategy. When larger numbers are used, students quickly realize that counting becomes inefficient and laborious. Hopping allows students to employ counting skills they are comfortable with, but increases rigor and mathematical practice.
Helpful hints:
Supply models and provide kinesthetic practice. Select appropriate number lines according to students’ individual needs. Some students will easily grasp hopping and will be able to use the open number line while others will need the patterned number line to see and count the 10’s and 1’s. Make a large patterned number line for kinesthetic learners and have them physically hop the numbers. Students will not only love this activity, the multi-modal approach reinforces learning.
Make Hailey pointers. Cut out and laminate Hailey patterns and use a hot glue gun to adhere to craft sticks. Students can use a Hailey pointer to hop the numbers in each problem.
Practice skip-counting. Some students struggle with skip counting and could benefit from repeated practice. Chanting by 100’s, 10’s and 1’s while walking in line, calendar time, even clean-up time all serve as great practice opportunities. Be sure to vary starting points so to ensure that students aren’t just counting by multiples of 100’s, 10’s or 5’s. (For example start at 57 and count by 10’s, then switch and count by 1’s.)
Be flexible with students’ hopping methods. Remember, the whole point of teaching strategies is to help students become fluid, flexible thinkers with deep conceptual understanding. While Hailey teaches students to start with bigger number and hop by 10’s and then 1’s, do not insist that students need to only hop this way. It is imperative to allow them to experiment and try multiple methods in order to find the most meaningful and efficient hopping method for themselves. Some hop to the nearest multiple of 10 and then continue hopping by 10’s, while others hop by all of the 10’s in one hop. Accept all methods if students solve problem correctly, explain method and apply across settings.